How to fix ”crawled - currently not indexed” in GSC
Explore all the reasons for the "crawled – currently not indexed" status on Google Search Console and find proven techniques to get your pages indexed by Google ASAP.
Updated May 23, 2025
AI Summary
“Crawled – currently not indexed” is one of the most common statuses on Google Search Console, but understanding the underlying causes and how to address them can be challenging.
In this article, I’ll explain the reasons behind this status and provide clear guidance on how to solve "crawled – currently not indexed." But first, let’s discuss what “crawled – currently not indexed” means and how it affects your website.
Key takeaways
- "Crawled – currently not indexed" is Google's way of dealing with low-quality content.
- Having over 5% "crawled – currently not indexed" pages can hurt your overall website ranking.
- If you have pages that aren't indexed, you need to take action.
- There are proven best practices to prevent and fix "crawled – currently not indexed."
TL;DR: How to solve "crawled – currently not indexed"
To fix “crawled – currently not indexed” in Google Search Console, follow these key steps:
- Improve content quality: Make sure your content provides value and targets search intent. Avoid thin, duplicated, or AI-generated content.
- Check for duplicate content or cannibalization: Merge similar pages or use canonical tags to show Google which one to index. Block pages that don’t need to appear in search (e.g., paginated pages) with a noindex tag and robots.txt rule.
- Audit your crawl budget and publishing velocity: If you’re a new site publishing too fast, slow down. Prioritize high-quality content and publish at a manageable pace to match your crawl budget.
- Fix technical SEO issues: Address soft 404s, missing metadata, broken redirects, sitemap issues, and other site health problems that could be affecting crawlability or indexability.
- Enhance internal linking and site structure: Optimize your site's internal linking and URL structure. Categorize the content correctly, and ensure each category is visible in the URL structure.
- Review your domain health and backlink quality: Check your domain for spammy backlinks, manual actions, or a history of abuse. Disavow harmful links and focus on building a trustworthy website.
- Clean up low-value or problematic URLs: Block URLs with UTM parameters or RSS feed URLs using robots.txt or a noindex tag if they don’t provide value.
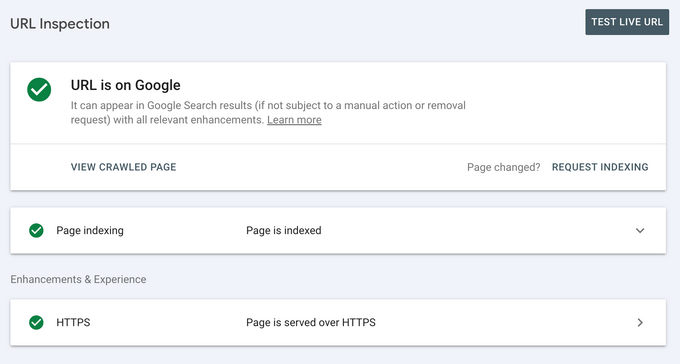
- Ask Google to recrawl the page: After making improvements, use the URL Inspection Tool in Google Search Console to request re-indexing by clicking “request indexing” or “validate fix.”
I'll discuss these steps in more detail below.
What does "crawled – currently not indexed" mean?
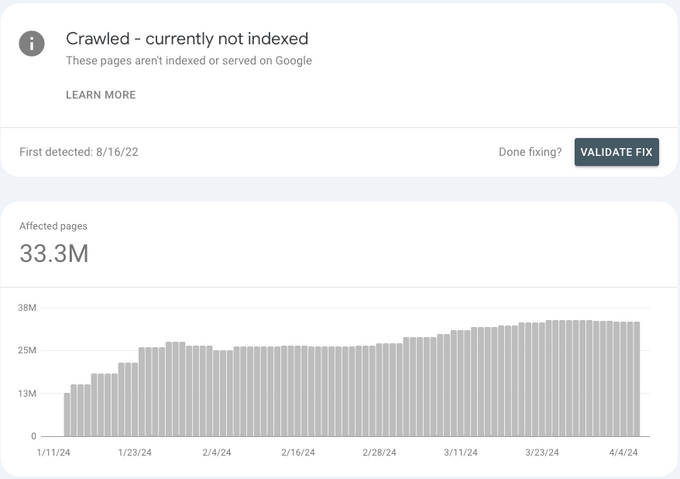
Google Search Console's “crawled – currently not indexed” status indicates Google's crawlers scanned your pages and decided not to include them in their index yet. Pages with this status do not appear in search results unless Google decides to index them sometime in the future.
This is a common issue for websites not indexed by Google. While they never mention the exact reasons for this, I've found it has to do with low content quality based on the types of pages they typically exclude.
So, if you publish content that's duplicated from a different website and doesn't provide value to your readers, Google won't index it. Other web pages address the relevant search queries better, and they don’t want to waste their crawl budget or resources indexing yours.
The implications of "crawled – currently not indexed" on your website
It’s normal to have pages that Google crawled and decided not to index. I've seen this on every site I’ve worked with. However, if over 5% of your pages aren't indexed, Google may see your site as low-quality, which could lead to a loss in rankings and, therefore, traffic.
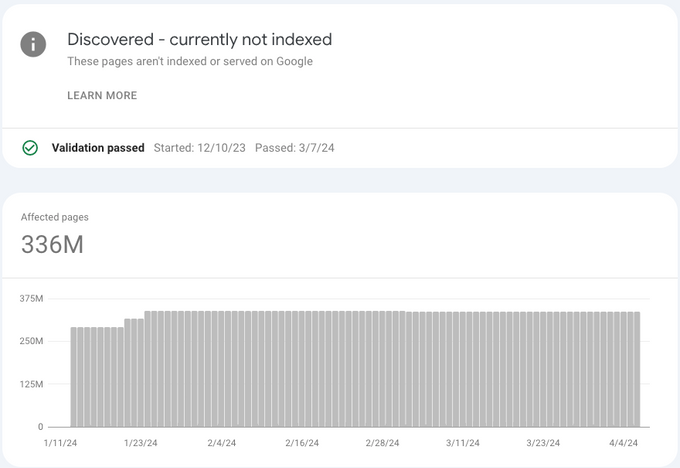
“Crawled – currently not indexed” vs. “discovered – currently not indexed”
The "discovered – currently not indexed" status means that Google found a page but hasn't crawled it yet. In other words, Google hasn't analyzed its content and therefore hasn't decided whether to index it or not.
In general, this status means that your content is even lower quality than crawled not indexed. I'd even go as far as to say it's a red flag for you as a site owner that you need to improve these pages.
Both “discovered – currently not indexed” and “crawled – currently not indexed” indicate that your content isn’t good enough to index. The difference is that Google knows your web pages exist, but they're not even going to crawl them because they know your content is usually low quality.
» Book a free consultation to fix your indexing.
9 reasons for “crawled – currently not indexed” and how to solve them
There are several reasons why a page is crawled but not indexed. Let's explore each reason, why it occurs, and how to fix "crawled – currently not indexed."
1. Poor content quality and inflation
Content quality and inflation of content are some of the main reasons for your content to be in the “crawled – currently not indexed” or “discovered – currently not indexed” statuses.
Low-quality content is essentially content that doesn’t provide the user with a satisfying answer to what they're searching for. Google can identify such content by reading it and recognizing that it's poor. They can also measure high bounce rates or instances where users search again after visiting a page.
Types of low-quality content include:
- Thin content: Pages that don’t provide enough value and in-depth information.
- Duplicated content and cannibalization: Content copied from other websites that doesn't add unique value. You may have duplicate content and keyword cannibalization in multiple places on your website.
- AI-generated content: Content generated by AI without any originality or value added to it.
- Content that doesn’t target search volume: Content that doesn’t target specific search queries or interest users.
- Similar pages: Near identical pages that don’t contain much content (e.g., user profile pages and pages for similar products).
- Spammy content: Content created using manipulative techniques, such as keyword stuffing or scraping content, to artificially boost website rankings.
- Too many ads: Pages containing an unreasonable amount of advertisements, leading to a poor user experience.
- Access restrictions or gated content: Content only accessible by performing a specific action, such as providing your email address or paying a fee.
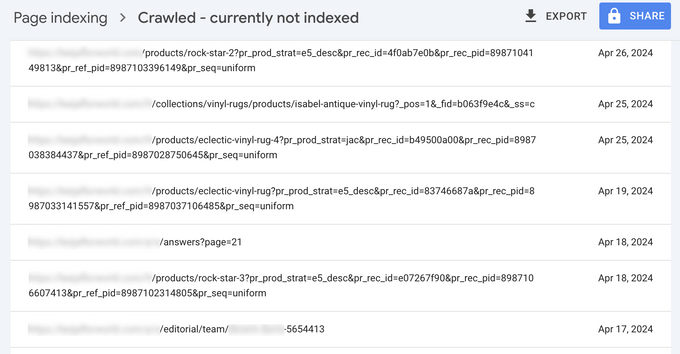
- Automated pages: Pages generated using automation for purposes such as displaying sports scores or scraping content from Amazon are not indexed by Google if they don’t provide significant value. The image below shows an extreme example of such a case that I've come across.
» Learn how to create content that converts.
How to fix it
In general, you can solve these issues by ensuring that every piece of content provides value—a content audit can help with this. Here's what to do in more specific cases:
- You have similar pages, but there's justification for having them: Consider not indexing every variation. Instead, you can index the overall collection or category page. Alternatively, merge these pages or block them from the index with a noindex tag and robots.txt rule. You may also want to link between these pages.
- Your website has duplicate content or cannibalization: Use canonical tags to point to the page you want Google to index. Alternatively, you can delete one of the pages or merge them.
- Your content doesn't target search volume: To check this, take the URLs of your unindexed pages, put them into ChatGPT, and ask it what keywords they target. Then, check if those keywords have volume or what other content ranks for them to see if your content is competitive enough to rank too.
- You're building pages with automation and want them indexed: Make sure each page is linked correctly and adds value to your website and the internet. If you're generating content with AI or there are many other pages like yours, there's no need for Google to index your content.
2. Crawl budget issues
Google may not index your content because of crawl budget issues. Crawl budget is a term coined by SEOs that refers to how many resources Google is willing to invest to crawl your website.
If you're a smaller or newer website publishing a lot of content very quickly, you don’t have a very high crawl budget because Google doesn't trust your site yet and won't index all of your content. This, of course, means you'll have pages under “crawled – currently not indexed” or “discovered – currently not indexed” that won’t get organic traffic.
Crawl budget issues occur for the following reasons:
Low domain authority
Disproportionate rate between crawl budget and content velocity
A sudden surge in content velocity
The specific page is too new, and Google hasn't crawled it yet
How to fix it
If you're a new website, you should either publish your content gradually or expect a lot of unindexed pages in the beginning. So, do your math and decide which option is better for you.
If you're already in this situation, you can reduce the velocity of content creation and ensure proper internal linking between your content pages. At the same time, invest in content quality and show Google you have a trustworthy website to increase your domain authority and crawl budget.
3. Technical SEO and overall site health
Some reasons for Google’s crawled, not indexed status may be related to technical SEO and other factors affecting your site’s health, like:
- Poor user experience: Pages or elements that load slowly or incorrectly on desktop and mobile devices, leading to bad user experience.
- Soft 404 errors: This happens when Google tries to crawl a website, and it returns a page that doesn't exist.
- No proper sitemap.xml: Without a proper sitemap, Google finds it more difficult to reach certain pages.
- Canonical tags: If your website's canonical tags aren't properly done, Google won't know which pages to give authority. This can also affect your website's crawl coverage.
- Redirect loops: A series of redirects that send traffic from one page to another in an infinite loop.
- Missing meta titles, meta descriptions, and schema markup: Not providing the information that helps Google understand what a page is about.
» Learn how to optimize your site for conversions.
How to fix it
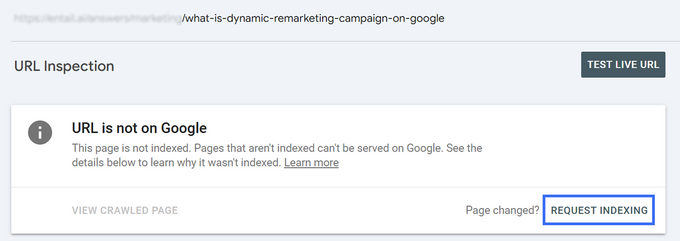
Site health encompasses many factors, so make sure everything on your site is working well. Regularly check the Page Indexing report and Crawl Stats report in Google Search Console, determine the reasons your pages aren't indexed, and decide how you want to take action.
After you fix those issues, you can ask Google to index these pages by clicking “request indexing” or “validate fix.” Then, keep track of these pages to see whether they disappear from the “crawled – currently not indexed” status.
Why validation keeps failing for "crawled – currently not indexed" pages
When you click “validate fix” in GSC, Google checks whether the issue you tried to fix has actually changed. For validation to succeed, the affected pages need to show a new status—for example, moving from “crawled – currently not indexed” to “indexed.”
If there’s no change and the pages are still in the same state, validation will fail. This doesn’t necessarily mean there’s something wrong with the pages—it just means the issue is still present. Once the pages are indexed, validation will show as successful.
» Let's fix your indexing. Book a call with an SEO expert.
4. Poor internal linking and site structure
If your website isn't structured correctly or there's not enough internal linking within your menus and content pages, Google won’t index them.
Some common internal linking and site structure mistakes include:
- Orphaned pages: These pages have no incoming links from other web pages, which signals to the algorithm that they aren't important.
- Poor site URL structure: This happens when your website's URL structure isn’t done right, and Google doesn't understand the hierarchy of your content.
- Pages duplicated by default: This includes tag pages, category pages, and pagination. For instance, if your blog has multiple articles and you have "blog/page1," "blog/page2," etc., these pages don't provide additional value or new content, and Google will choose not to index them.
- Expired product pages: This refers to pages for products that you're not selling anymore or have been out of stock for a while.
How to fix it
With these issues, the problem basically indicates the solutions. You need to make sure your website's entire URL structure makes sense, the content is categorized correctly, and these categories are visible in the URL structure.
In addition, make sure you don't have any expired products on your website. If you have duplicated pages, remove them and improve internal linking on your website.
» Get perfectly SEO’d pages out of the box with Entail’s no-code page builder.
5. Poor domain health
If your domain health is poor, Google may view it as problematic or unreliable. As a result, they might not want to index your content.
Reasons for poor domain health may have to do with:
- Site history, penalties, and manual actions: This often occurs when you purchase a domain that was involved in manipulative or abusive SEO practices, such as spamming, malicious link building, creating satellite websites, etc.
- Low-quality backlinks: Your site could be the target of a link attack, where somebody creates spam links to your website, or you may build low-quality links that Google marks as spam.
- Fraudulent content: This refers to content used to deceive users, such as publishing false product reviews to get people to buy a product.
How to fix it
To improve domain health, begin by addressing the quality of your backlinks. Use tools like Ahrefs to identify harmful backlinks and disavow them through Google Search Console.
Then, focus on improving the quality of your content and really making sure your website is working to show Google that it's trustworthy.
6. URL parameters
URL parameters often lead to duplicated content, which leads to these pages being crawled but not indexed.
Examples of URL parameters include:
- UTM tags
- RSS feed URLs
- Category pages
- Topic pages
- Paginated URLs
These pages typically replicate existing content by linking to other articles without adding unique value on their own.
How to fix it
To fix this issue, add content to pages with URL parameters. For example, you can include relevant information on a category page so that it provides value rather than just a list of links.
If you have URLs with UTM parameters or RSS feed URLs, you should block them by adding a robots.txt rule so Google's crawler stops indexing them.
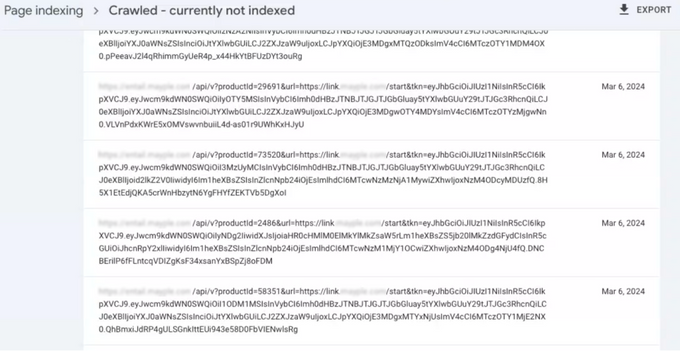
7. API pages and private-facing content
API pages and private-facing content (e.g., development environments or admin dashboards) are also possible reasons for “crawled – currently not indexed.”
These pages aren't supposed to be indexed. However, if they're accessible, Google might crawl but not index them because they don't provide value.
How to fix it
To solve this, block Google's crawler from reaching any API pages or private-facing content by adding rules to your robots.txt file. You can also add a noindex tag to these pages.
Keep in mind that suddenly blocking many pages that have been indexed for a long time may also have a negative impact because you never know how Google will respond to extreme changes. In this case, you may want to start slowly removing some from the index and making sure that it doesn't impact anything else.
» Talk to an SEO expert to fix your indexing.
8. Blocked pages
You may have pages with noindex tags, canonical tags, or blocked by robots.txt. These pages aren’t supposed to be indexed. However, sometimes, they might still appear in the crawled but not indexed category.
Should you fix it?
Generally, these pages are supposed to be excluded from the index anyway, so you don’t have to take any action.
9. Bugs
Lastly, your pages might appear in the “crawled – currently not indexed” status due to a bug. So, this status might inaccurately reflect the indexing of your content.
For example, your pages may be reported as crawled but not indexed. However, if you perform a site crawl and look for the URL, it indicates that the content is indeed indexed. This is known as a false positive.
You can use Google Search Console's URL inspection tool to determine whether a page is indexed or not.
Should you fix it?
Because your content is actually indexed, there’s nothing you need to do about this.
Solve and prevent “crawled – currently not indexed”
While there may be other reasons for having your content crawled but not indexed, these are the instances I see most often. If you apply the guidelines I’ve shared, you can get your pages indexed and prevent other pages from falling into the "crawled but not indexed" status in the future.
FAQs
What is “crawled – currently not indexed”?
It means Google has seen your page but decided not to include it in search results.
How do I fix crawled but currently not indexed?
Improve content quality, fix technical or structural issues, and use proper internal linking. Then, request validation in Google Search Console.
Does "crawled - currently not indexed" hurt SEO?
Yes, because unindexed pages won't appear in search results, which decreases visibility and organic traffic.
How do know which pages are crawled but not indexed?
Use the Page Indexing report or URL inspection tool in Google Search Console.
How long does it take for Google to re-index my pages?
It can take anywhere from a few days to several weeks after fixes are implemented and validated, depending on your site’s crawl rate and authority.