Website not getting indexed? Here's why and how to fix it
Find out why Google isn't indexing your site and learn proven techniques to get your pages back in their index.
Updated May 23, 2025
AI Summary
Indexing issues have become increasingly common, particularly with the rise of AI-generated content. These problems can affect anything from a few pages to an entire website. Fixing indexing issues is key to SEO success and can greatly improve your site's visibility and organic traffic. To do this, you need to identify and address the root causes, keep your Google Search Console reports clean, and improve your site's overall performance. While it may take some time and effort, the results are well worth it.
Key takeaways
- There are many reasons why your website may not be indexed, but almost all can be identified and fixed.
- Even websites that have been seriously penalized by Google can recover, so don't lose hope.
- The first step to fixing indexing issues is researching and identifying the root cause.
- In SEO, it's crucial to keep your Search Console statuses clean and aim to have the minimum number of issues possible.
How Google indexes your pages
Google indexes content based on the keywords it targets in an effort to show relevant results for user searches. This ensures that when people search for information, Google can display the best possible search results.
Key factors affecting indexing include:
- Relevancy: Each page needs to be relevant to specific searches. Google looks at how relevant your content is compared to other sources to decide where to put it in search results.
- User journey: Your content should also help visitors complete their user journey with relevant calls to action and complete information. This will help users finish their search without going back to Google or bouncing off your page.
- Content quality: Google judges content quality based on your specific industry or vertical. Your content needs to be better than that of your competition to rank well.
- Links: Quality links significantly influence how Google evaluates and ranks your content. This includes external links to your content and internal links within your site.
- Technical factors: Technical factors also affect indexing, such as the speed of your site, schema markup, readability of your content, mobile experience, structure of your site, and navigation.
The main reason pages don't get indexed is that Google thinks the content isn't valuable enough. Getting your site or web pages indexed starts with identifying the specific issues that affect the value of your content.
Why some pages don't need to be indexed
Sometimes, Google doesn't index your content for reasons you might have set up on purpose or by accident. For example:
- Gated content: Google can't access content if users need to enter an email or log in to view it.
- Noindex tags: These are tags that developers or SEOs add to tell Google not to index certain pages.
- Canonical tags: If you have two very similar pages, these point Google to the main page while the other goes unindexed.
- Blocked in robots.txt file: The robots.txt file tells search engine bots which pages to index or not index on your website.
- 301 or 302 redirects: This is like telling the post office (or Google) to send your mail to a new address. Eventually, Google will stop visiting the old address and send traffic to the new one.
Pages that fall into these categories don't need to be indexed. However, I've seen websites accidentally block Google from indexing their whole site or big parts of it in the robots.txt file. This is why it's a good idea to check these settings often to make sure only the content you want to hide is being hidden.
» Speak to an expert to start fixing your indexing.
Common indexing issues and their solutions
Google uses various statuses in Google Search Console to categorize non-indexed pages. Let's look into each one, why they happen, and how you can fix it. I'll also discuss a few others that Google doesn't explicitly mention.
Crawled – currently not indexed
Google invented the "crawled – currently not indexed" status to manage content inflation and low-quality pages. This status affects websites of all sizes, with larger sites potentially having millions of pages in this category.
While there are many different reasons for receiving this status, it's mostly due to thin content that doesn't provide value. If your website is technically sound but still has indexing issues, it's likely due to poor content quality.
Discovered – currently not indexed
"Discovered – currently not indexed" is a status similar to but worse than "crawled – not indexed." In this case, Google knows your pages exist but chooses not to crawl them. This status often indicates more serious issues with content quality or website structure.
» Fix crawled and discovered not indexed ASAP. Book a free call with an SEO expert.
Alternate page with proper canonical tag
As I mentioned earlier, adding a canonical tag to your pages tells Google which is the main version. The alternate unindexed page will fall into this category.
Should you fix it?
This isn't necessarily a problem. It's working as intended if the canonical page is the one you want indexed.
Duplicate, Google chose different canonical than user
What's happening here is that Google's algorithm has decided that a different page covers this topic better than the one you specified. So, Google chose a canonical that was different from what you provided.
How to fix it
- Review your content structure.
- Check for and fix keyword cannibalization.
- Strengthen the content on the page you want to be canonical.
» Let's fix your indexing. Chat with an SEO expert.
Duplicate without user-selected canonical
This happens when Google finds duplicate content on your site, but you haven't added a canonical tag to indicate which is the main page. Google then decides not to index this content to avoid duplication.
How to fix it
- Use canonical tags to tell Google which page is the main version.
- Check for and fix keyword cannibalization.
Blocked due to unauthorized request (401)
Google's crawler cannot access this page because it's unable to provide the authentication credentials your server requested. Google can't crawl and index password-protected pages or gated content.
How to fix it
- If you want this page indexed, remove authentication requirements for Googlebot.
- If you don't want this page indexed, keep the authentication requirements in place and add a noindex tag or block the page in your robots.txt file.
Blocked due to access forbidden (403)
This status indicates that Google tried to crawl a page but was denied access. This can happen due to permission issues, a misconfigured .htaccess file, IP address blocking, or authentication restrictions.
How to fix it
- Review your website's .htaccess file, server configurations, security plugins, firewalls, and robots.txt file to find any rules blocking Google's crawlers.
- Remove or adjust any rules blocking access.
- Use the URL inspection tool in Google Search Console to make sure Google can now access your pages.
» Book a free consultation to fix your indexing.
Soft 404
These pages display a "not found" message to users but incorrectly return a status code other than the proper 404 HTTP response code to search engines.
Soft 404s waste your crawl budget because Google tries to index pages that no longer exist. So, be sure to fix these pages as soon as possible.
How to fix it
- Check the list of soft 404 pages.
- If they've moved, delete them and add a 301 redirect.
- If they've been deleted, use a 410 redirect.
Not found (404)
This error occurs when pages are not found, usually because they've been deleted or removed. Google will eventually forget about these pages, but it'll take time.
How to fix it
- Add a 301 redirect if the content has moved.
- Redirect to a relevant page (e.g., the category page for a deleted blog post).
- Use a 410 redirect to indicate the page has been permanently deleted.
» Get an SEO expert to take care of your indexing.
URL blocked due to other 4xx issue
This status appears when a URL returns a client-side error besides the 401, 403, 404, or soft 404 errors we've already mentioned, preventing Google's crawler from accessing the page. There are many other 4xx client errors, including bad request (400), payment required (402), method not allowed (405), not acceptable (406), and proxy (407).
How to fix it
- Each 4xx error tells a different story. Use your server logs or tools like Google Search Console and Chrome DevTools to pinpoint exactly what's going on and decide how to proceed.
- If you can't find a viable solution, you can implement a 301 or 410 redirect.
This status can be tricky, so it might be a good idea to chat with a developer or your hosting provider to resolve it quickly.
URL blocked by robots.txt
This status appears when your robots.txt file prevents Google from crawling certain pages.
How to fix it
This is usually deliberate, but you can review your robots.txt file to ensure you're not accidentally blocking important pages.
URL marked 'noindex'
When you deliberately add noindex tags to certain pages, you're telling search engines not to index them.
How to fix it
This isn't a problem if it's intentional, so ensure you're using noindex tags correctly.
Redirect error
Redirect errors happen when a website fails to send users or search engines to the right webpage. According to Google, this can occur because of:
- A redirect chain that's too long
- A redirect loop
- A redirect URL that exceeds the max URL length
- A bad or empty URL in the redirect chain
How to fix it
- Double-check your redirect rules to ensure there are no chains or loops.
- Find and fix any poor URLs or broken links.
» Chat with us to get your web pages indexed.
Server errors (5xx)
This happens when your server encounters a 500-level error while trying to fulfill a request.
How to fix it
- Review your server logs and restart your server.
- Disable any faulty plugins.
- Check for any errors in your .htaccess file.
- Ensure your server and website configurations are correct and up to date.
- Get in touch with your hosting provider if needed.
Your website is too new
When your website is new, Google doesn't know who you are yet. This lack of trust can lead to slower indexing and ranking because:
- Google needs time to trust your website. This is partly to prevent spam tactics where people create legitimate-looking pages, get them indexed, and then change them to misleading or malicious content.
- Your site's reputation builds over time. Even with lots of content, a new site lacks the track record Google uses to evaluate trustworthiness.
- New sites often lack the external signals (like backlinks or social media mentions) that Google uses to assess relevance and authority.
How to fix it
You don't need to do anything. In SEO, it typically takes about six months to start seeing the initial effects and around 12 months for more significant results. This is standard. However, you can use the following strategies to make sure Google indexes your new site:
- If your site is associated with an established brand (like a Shopify subsidiary), you should link from the main website to the new one and use consistent branding to show the association.
- If your website covers highly trending topics in a unique way, it might be indexed more quickly.
- Build external signals. Try to get links from other reputable websites. Engage on social media to increase visibility and mentions. Create content that naturally attracts attention and links.
- Make sure your site is well-structured, fast, and follows SEO best practices from the start.
- Regularly publish original content to show Google your site is active and valuable.
- Use Google Search Console to submit your sitemap and monitor indexing.
Remember, while these strategies can help, building trust with Google takes time. Focus on creating value for your users, and indexing and ranking should follow naturally as your site establishes itself.
Penalties
Google can penalize your website without notifying you. These penalties can lead to de-indexing and cause dramatic traffic drops, sometimes to near zero. Common reasons for this include duplicating content from other sites (e.g., copying data from Amazon), malicious link building, spamming, cloaking, etc. It may even happen because you've purchased a domain that has a negative history with Google.
If only your homepage is indexed, it may suggest that Google has penalized your site.
How to fix it
- Improve the quality of your backlinks.
- Create high-quality, original content that follows Google's guidelines.
- Ensure your website works well and provides a good user experience.
If you've been penalized, you can recover, but it'll take some time and effort to regain Google's trust.
» Book a consultation to get rid of penalties affecting your indexing.
Poor internal linking structure and navigation
Poor website navigation and internal linking structure can make it difficult for Google to find and index your pages. It's like a shopping mall without signs; if Google can't find your "ice cream shop," it won't be indexed.
How to fix it
- Create a clear, logical site structure with good internal linking.
- Use your website's header and footer to link to important pages.
- Ensure your logo links back to the homepage on all pages.
- Categorize your content correctly. These categories should be visible in the URL structure.
Missing or incorrect sitemap
Adding your sitemap to Google Search Console helps Google understand your website structure. It shows Google all your pages, making it easier for the search engine to find and crawl them. If your sitemap is working correctly, Google can identify all your pages more efficiently.
How to fix it:
- Add your sitemap to Google Search Console.
- Ensure your sitemap is up to date and includes all important pages.
- Make sure Google can access and crawl the pages listed in your sitemap.
Technical SEO issues
Technical issues related to schema markup, meta titles, and meta descriptions can also affect indexing. If these elements are missing or incorrect, Google will likely choose not to index the page.
How to fix it
- Ensure all pages have proper metadata that accurately reflects the content to help Google understand what the page is about.
» Get perfectly SEO'd pages out of the box with Entail's no-code page builder.
Poor page experience
Google considers page experience when indexing websites. This includes factors like page speed, how elements load, and mobile performance. If your site offers a poor experience, Google may choose not to index it.
How to fix it
- Improve your overall site health by making sure everything works well, including page speed, site security, mobile-friendliness, easy navigation, etc.
- Work with a developer to enhance the overall website experience.
How to check if a page is indexed
To check if a page is indexed, start by searching for your page or site directly on Google using "site:" followed by the URL.
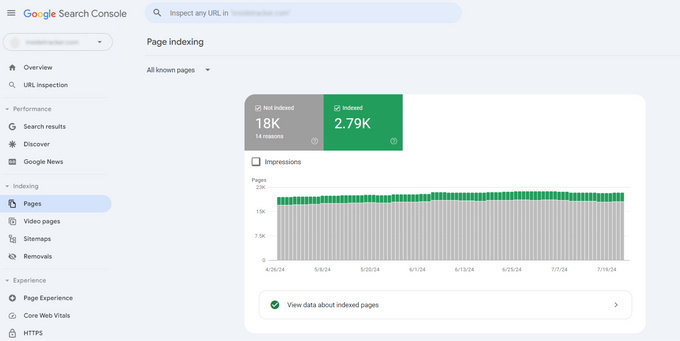
You can also use Google Search Console's Page Indexing report to view non-indexed pages, though this report is limited to 1,000 pages per category.
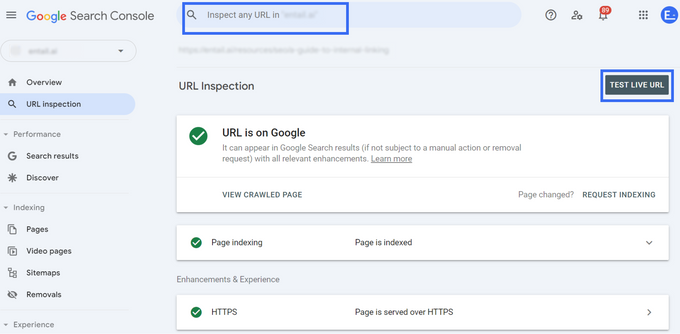
For a specific URL, use the "Inspect URL" feature in Search Console by entering the URL in the top search bar.
Always click "Test Live URL" for the most up-to-date status. This step is particularly important if you've recently fixed indexing issues, as Google may take time to recognize these changes.
» Let's fix your indexing. Book a call with an SEO expert.
How to tell Google you've fixed an indexing issue
Once you've taken care of the issues causing your page not to be indexed, you can head to Google Search Console and click "validate fix" or "request indexing." You can also use Google Search Console's API to request indexing.
Having said that, I think this has little real effect. The algorithm decides what to index, and simply asking Google to index your pages doesn't do much. What matters most is fixing the underlying problems that prevent indexing.
How long does it take to get indexed again?
It's hard to predict how long it takes for pages to get indexed, so you need to monitor it yourself. You can check daily, but keep in mind you won't see any changes for at least 24 hours. Often, it can take weeks or even months to see improvement.
Provide value and indexing will follow
Completely de-indexed websites or new pages that struggle to get indexed can overcome these challenges. The key is building a reputable brand with high-quality content that provides genuine value to users. Google's ultimate goal is to index websites that benefit their users. If your website offers real, tangible value, it will eventually be indexed.
» Get your website indexed on Google with Entail. Speak to an SEO expert now.