Ask Google to index your site: A step-by-step guide for faster indexing
Learn how to get Google to index your site and improve your chances of being indexed.
Updated May 23, 2025

AI Summary
Google's index is a massive digital library of web pages that Google uses to find and show relevant search results. Getting your website indexed means making sure Google knows it exists and can include it in its library. This can be a complicated process but don't worry. I'll walk you through the steps of asking Google to index your site and share practical tips to ensure your pages get indexed.
Key takeaways
- Use Google Search Console to check if your pages are indexed.
- Identify and diagnose why your pages aren't indexed before trying to fix them.
- You'll need to take different measures depending on whether your website is new or already established.
How to check if your site is indexed
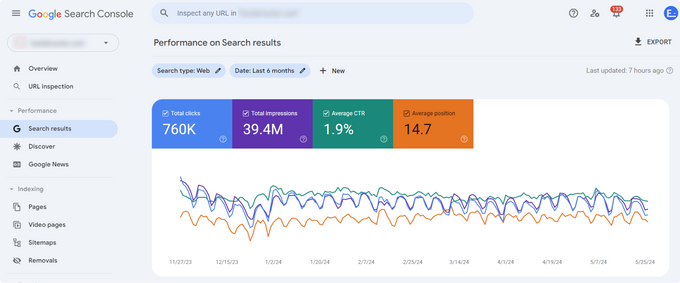
Google Search Console is the best place to check whether your site is indexed. To get started, select a time frame in the "Search results" section—usually three to six months—and look at how many pages have impressions.
Take note of the following:
- How many pages appear in search results
- How many queries are indexed
The number of indexed queries and the trend of search queries over time are strong indicators of your site's health and indexing status. You can use this information to see how many and which pages of your website are indexed.
READ MORE: 10 proven techniques to fix "Discovered – currently not indexed"
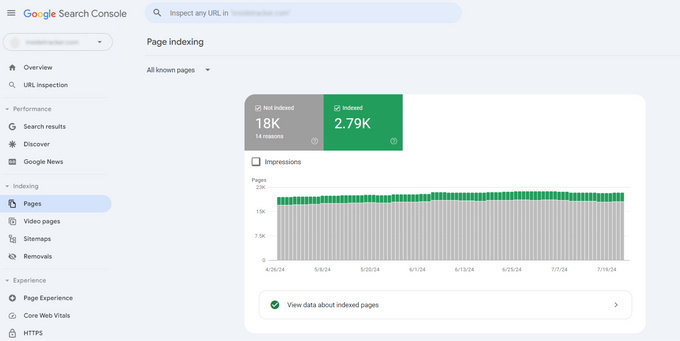
Use the page indexing report
You can use the page indexing report to view the total number of indexed pages (in green) and unindexed pages (in gray) on your website. Sort by the number of pages to see the reasons why some of your pages aren't indexed.
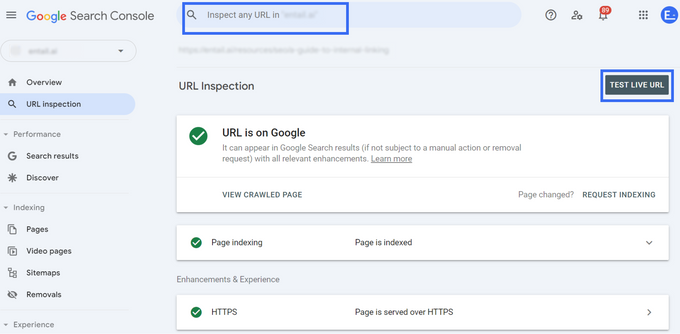
URL inspection tool
To check if a specific page is indexed, use the URL inspection tool. Once you enter the URL into the search bar, Google will tell you if the page is indexed or not.
But this alone isn't enough because the data may be outdated. For the most current data, click "test live URL" to see if the URL is on Google and if Google can access it.
» Talk to an SEO expert to get your site indexed.
How to get indexed by Google
Getting your site indexed by Google can depend on several factors, including the type of site and how long it's been up and running.
New websites
Build a good reputation online
The main challenge for new websites is earning Google's trust. Since Google's algorithms can't inherently know which sites are trustworthy, it takes time for new sites to build that trust. This means your pages might not be indexed immediately. To speed up the process and get your new website indexed quicker, you need to show Google signals that indicate your website is legit and adds value.
For example, if you have a well-known brand with a lot of traffic and you want to start a smaller brand, you can link to the smaller brand from the larger one. This shows Google that the smaller brand is associated with a trusted and established site.
Increase branded traffic
Getting people to search for your brand also sends a strong signal to Google. For instance, you can drive traffic through paid search, ads, social media, or other sources. This exposure leads to more people searching for your brand, which in turn boosts your branded searches. This way, you'll likely rank high in search results, signaling to Google that your site is trustworthy.
Create high-quality content for SEO
Even if you're driving a lot of traffic to your website, you may not rank well if it doesn't have high-quality content that targets specific search intent or search volume.
Your site might get a lot of branded traffic, but if your content doesn't target broader search terms, it won't attract non-branded traffic. While a lot of branded traffic may lead Google to index your site quickly, it will primarily index pages related to your brand, not those targeting informational queries, which make up most of the traffic on the internet.
Established websites
Avoid low-quality, thin content
If your website contains low-quality or thin content, Google may decide not to index it. In fact, these pages often end up in the crawled but not indexed status in Google Search Console.
To avoid this, you'll need to ensure all your content is high-quality, provides value, and meets your audience's needs. You should also try to minimize AI-generated content and keyword cannibalization.
Target search volume
There can also be older websites that don't target high search volume or don't have much content, giving Google little reason to index them. In such cases, you'll need to start creating high-quality, relevant content for your website that targets specific searches to improve its chances of being indexed and ranking well.
Ensure Google can discover your pages
If your website isn't getting indexed, it might be due to discoverability issues. Google has two main ways of discovering new pages. The first way is through your sitemap, which tells Google what pages exist on your site.
The second way is through links. It can be internal links within your content or other websites linking to you. If there are no links, Google won't find your pages. To ensure your pages are discoverable, you need to link to them from other relevant pages that also have traffic using relevant anchor text.
Get links from other websites
Another option is to get links from other websites. However, be careful not to overdo it or manipulate the system, as Google penalizes sites that engage in link manipulation. Proper linking from other websites will definitely improve indexation.
» Let's get your site indexed. Chat with an SEO expert.
How to ask Google to index your site
Asking Google to index your site is fairly simple, but its effectiveness largely depends on your site's quality and technical health. So be sure to fix any issues before following these steps to ask Google to index your site:
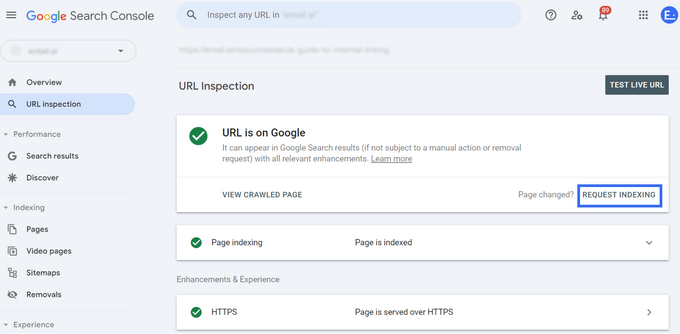
- Go to Google Search Console.
- Navigate to the URL inspection tool and enter the relevant URL.
- Click "request indexing."
While requesting indexing is useful if you've resolved a technical issue and need a fresh crawl, it's not a cure-all solution. If Google isn't indexing your pages, you need to understand why and address the root cause. Simply requesting indexing won't help if your pages have underlying issues.
» Chat with us to identify and solve indexing issues.
Common indexing issues and how to fix them
There are several reasons why Google might not index your website. Understanding and addressing these issues can improve the chances of Google indexing your pages:
- Blocked by robots.txt: The robots.txt file tells Google which pages to crawl or ignore. If your content is blocked here, it won't be indexed. Check the robots.txt report in Google Search Console under Settings → Crawling → robots.txt to ensure important pages aren't blocked.
- Noindex tags: Pages with a noindex tag won't be included in Google's index. Use the URL inspection tool or page indexing report in Google Search Console to check for unintended noindex tags.
- Poor internal linking: Ineffective internal linking makes it difficult for Google to find and index your pages. Make sure your website's URL structure is logical, content is properly categorized, and these categories are reflected in the URLs.
- Crawl budget issues: If you're out of crawl budget, Google may not index your new content, especially if you have many existing pages or frequently add new ones. Try to maintain a balance between your traffic and the amount of new content you create.
- Site structure and discoverability: If Google can't discover your pages, they might not get indexed. To fix this, submit an updated sitemap to Google Search Console and use clear internal and external links with descriptive anchor text.
- Technical SEO and site health: Poor user experience, soft 404 errors, missing sitemaps, redirect loops, and missing metadata can affect indexing. Make sure your site functions well by regularly checking the Crawl Stats report in Google Search Console to identify the reasons for non-indexing and take appropriate action.
Get Google to index your site
Ensuring Google indexes your website is crucial for it to show up in search results. While it can seem daunting, it's definitely achievable. Focus on creating great content, achieving a solid site structure, and making your pages easy for Google to find. By paying attention to these aspects, you can significantly boost your chances of successful indexing.
» Still not getting indexed? Book a consultation with an SEO expert to find and fix any issues.