How schema markup drives real business growth in 2026
Unlock visibility, CTR, and revenue with schema markup. Learn how structured data fuels SEO, AI citations, and measurable business growth.
Updated August 19, 2025

AI Summary
In 2026, structured data isn’t just an SEO “nice-to-have"; it’s a cornerstone of how search engines and AI models understand, trust, and surface your content. Schema markup has evolved from a tactic to earn prettier search snippets into a critical business growth driver, helping brands secure AI citations, improve click-through rates, and connect their expertise to measurable revenue.
This guide will walk you through what schema markup is, why it matters for both SEO and GEO, and exactly how to implement, maintain, and leverage it to grow your business.
Key takeaways
- Schema markup has shifted from an optional SEO tactic to a core business growth lever.
- It fuels both SEO (rich results, CTR boosts) and GEO (AI citations, reduced hallucinations).
- E-E-A-T-aligned schema builds long-term trust and authority.
- Ongoing maintenance prevents schema decay and keeps your content AI-ready.
- Schema directly impacts qualified traffic, conversion rates, and revenue attribution, giving you proof that SEO is driving business outcomes.
What is schema markup?
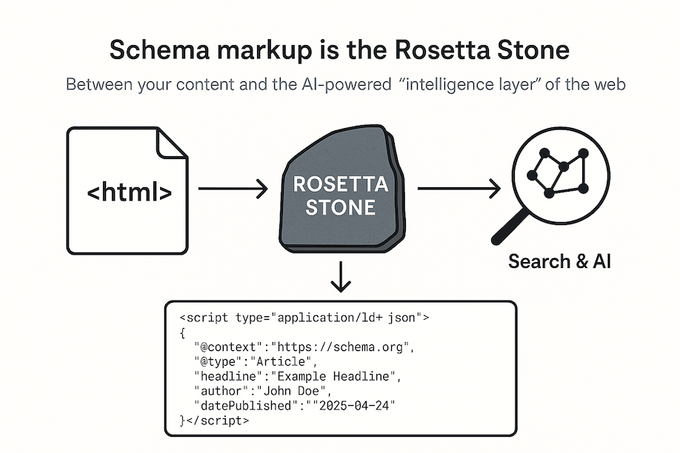
Schema markup is structured data; machine-readable code you add to your website’s HTML to clearly tell search engines and AI systems what your content means. It uses a shared vocabulary (schema.org) to classify elements like articles, products, reviews, FAQs, events, and more.
Think of it as the Rosetta Stone between your content and the AI-powered “intelligence layer” of the modern web. Without it, search engines and LLMs must guess, interpret, or not index your content. With it, they can verify details, extract answers, and present your brand in rich, high-visibility formats.
Why is schema markup so important since the rise of GEO/AEO?
In the pre-AI era, schema markup was mainly valued for unlocking rich results like star ratings, FAQ dropdowns, and product prices—features that expanded your search footprint and improved click-through rates. Those benefits remain, but the real shift today is its role in GEO.
» Learn how to improve CTR with SEO A/B testing.
Schema provides exactly that clarity, dramatically increasing your chances of being cited in AI answers.
For revenue-driven teams, this translates into more than just visibility:
- Rich results increase qualified organic traffic by setting accurate expectations before the click.
- Clear E-E-A-T signals (who wrote the content, why they’re credible, how the information is verified) reduce friction in the customer journey and improve conversion rates.
- Citations in AI answers strengthen brand authority and put you in front of buyers earlier in the decision cycle—generating demand that competitors may never see.
That trust reduces friction in the customer journey, lifting conversion rates. For brands, it means greater authority in emerging AI-led search experiences.
In short, schema markup has evolved into a growth content marketing lever that spans both traditional SEO and AI visibility. It's essential if you want your content to be seen, trusted, and acted on in the next era of search.
Schema markup language and formats
Schema markup is implemented as code added to your website’s HTML, using a standardized vocabulary from schema.org. While there are multiple formats supported by Google, your choice will depend on your platform and technical constraints.
The primary formats and languages for implementing schema markup include:
- JSON-LD is the preferred method for most use cases. It keeps structured data separate from your main HTML, making it cleaner, easier to maintain, and less prone to errors during content updates. It’s also the format Google recommends and supports most fully across its rich result features.
- Microdata and RDFa are inline approaches where schema properties are embedded directly into HTML tags. These formats can be useful if your CMS or platform doesn’t allow easy insertion of standalone JSON-LD scripts, but they’re more cumbersome to manage at scale.
Regardless of the format you choose, the key is accuracy and completeness. Your schema should reflect exactly what’s visible on the page, include all relevant properties, and use proper nesting when combining multiple schema types (e.g., FAQPage nested within HowTo).
Types of schema markup
Not all schema types deliver the same value, especially if your goal is to appear in AI Overviews and other generative search features. For maximum impact in 2026, prioritize the schema types that feed AI models clean, structured, and trustworthy information.
FAQPage
One of the most direct pathways into AI Overviews and Google’s “People Also Ask” boxes, the FAQPage schema structures your content in a Q&A format that AI systems can easily lift and cite. If you include an FAQ section within a HowTo article, make sure the HowTo is the primary schema and the FAQPage is nested as secondary.
HowTo
Ideal for guides and tutorials, the HowTo schema breaks complex processes into numbered, digestible steps. This is exactly how LLM models like to present instructions.
Article / blogposting
Essential for blogs and thought leadership content, Article schema identifies the headline, author, publication date, and main topic. This metadata helps AI evaluate the freshness and authority of your content.
Organization & person
This is foundational for building E-E-A-T signals. Organization schema defines your brand entity, official site, and social profiles, while Person schema links authors to bios, LinkedIn profiles, and other publications. Together, they form a connected knowledge graph that boosts long-term credibility.
Product & review
Critical for e-commerce, Product schema details name, description, price, and availability, while Review schema adds ratings and testimonials. AI often cites this data when recommending products, making it a high-value addition for transactional queries.
READ MORE: 9 high-impact content marketing strategies for e-commerce
VideoObject
If you create video content, VideoObject schema helps AI understand its topic, length, and key moments, improving your chances of being featured in rich video snippets or cited in AI summaries.
LocalBusiness
For brick-and-mortar operations, LocalBusiness schema ensures AI and search engines can provide accurate address, hours, and contact details in “near me” searches.
How to add schema markup to your website
The simplest and most efficient way to implement schema markup depends on your tech stack, team skills, and publishing workflow. For most users, especially those on WordPress, a robust SEO plugin is the fastest path to getting started.
Use a CMS plugin
Plugins like Rank Math or Yoast SEO can automatically generate core schema types (e.g., Article, WebPage) and give you user-friendly options to add more complex markup, such as FAQPage or HowTo, without touching code.
Pro tip: If you use a custom CMS, consider integrating schema creation directly into your publishing workflow. Our headless CMS can auto-generate relevant schema based on content fields. This ensures consistency and reduces the risk of errors or schema decay.
Leverage a schema generator
Free tools like Merkle’s Schema Markup Generator let you quickly create schema code for specific content types without hand-coding. You can then paste this directly into your site’s HTML or a tag manager.
Test before publishing
Before any schema goes live, run it through Google’s Rich Results Test to check eligibility for enhanced SERP features, and through the Schema Markup Validator to ensure it meets the full schema.org vocabulary standards.
Schema markup best practices
Getting schema markup onto your site is only the first step. Maintaining quality, accuracy, and strategic value is what drives long-term results in both your GEO and SEO goals.
Prioritize high-impact pages
Start with your most authoritative or highest-traffic pages. These will see the biggest lift from rich results and AI citations.
» Learn how to increase your SEO conversion rate.
Match schema to visible content
Never add markup for information that isn’t actually on the page. Misrepresenting content can lead to penalties and erode trust with both users and search engines.
Prevent schema decay
Audit your schema quarterly, or immediately after major site updates or redesigns, to ensure it’s still accurate. Outdated structured data that no longer matches your visible content can hurt performance and credibility.
By making that cycle part of your team’s standard operating procedure, you protect your search presence, strengthen your brand’s credibility, and keep a steady pipeline of qualified traffic flowing from both SEO and GEO channels.
Go beyond the basics
Don’t just add the minimum required fields. Include as many relevant properties as possible, such as <reviewCount>, author, publisher, and <dateModified>. Rich, complete data gives AI more context and improves citation likelihood.
Strengthen entity relationships
Use the <@id> property to link related entities across your site. For example, connect an Article’s author property to a Person schema on their bio page, and link that Person back to your Organization schema. This builds a strong knowledge graph that AI models trust.
How to check your website’s schema markup
Verifying that your schema is valid, accurate, and functioning as intended is essential for maintaining search and AI visibility. Make validation and monitoring part of your regular publishing process.
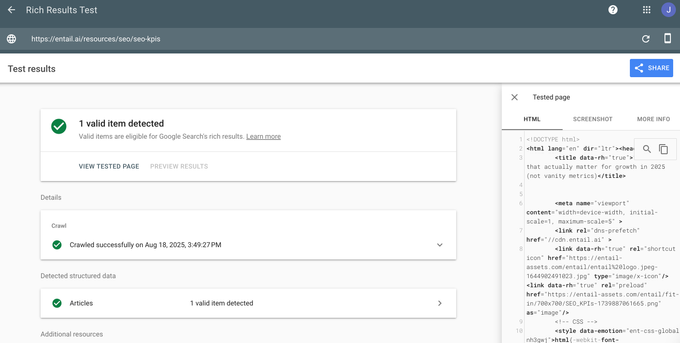
Google’s rich results test
This is your first line of defense. It confirms whether your markup is eligible for enhanced SERP features and flags errors or missing properties that could prevent your content from displaying rich results.
Schema markup validator
Use this tool alongside Google's Rich Results Test to validate against the full schema.org vocabulary—not just the types Google currently supports for rich results. This helps catch subtle issues that might still limit how AI interprets your data.
Manual code review
Always have a human review the generated JSON-LD to ensure it exactly reflects the content on the page. Watch for false claims, outdated details, or hidden data. These can harm credibility and lead to manual actions.
Ongoing monitoring in Google Search Console
Check the Enhancements report weekly for errors or warnings by schema type, and use the Performance report to compare CTR and impressions for pages with and without schema markup. Drops in performance can signal a markup issue that needs attention.
Make schema a habit, not a project
The real ROI of schema markup comes when it’s built into your publishing workflow, not treated as a one-off optimization. Every time you create, update, or refresh content, adding or reviewing schema should be a standard step in the process.
When schema is habitual, you’re continuously reinforcing your visibility in both traditional search and AI-driven experiences. You’re also preventing schema decay, ensuring that the information search engines and LLMs read from your pages always matches what users see.
Embedding schema into your CMS and workflow is the difference between an SEO experiment and a growth strategy. Entail is designed to make that habit automatic, so your team focuses on strategy, not markup maintenance
» Measure and improve ROI from SEO with the best SEO ROI tool.
FAQs
What is schema markup?
Schema markup is structured data—machine-readable code you add to your website’s HTML—to clearly tell search engines and AI systems what your content means. It uses the schema.org vocabulary to classify elements like articles, products, reviews, FAQs, and more.
Is schema markup still important?
Yes. It remains a key driver of rich results in SEO and is now critical for generative engine optimization (GEO), increasing your chances of being cited in AI Overviews and other AI-powered search experiences.
What are the benefits of schema markup in SEO?
For SEO, schema can unlock review stars, FAQ dropdowns, product pricing, and how-to guides directly in SERPs—boosting visibility and click-through rates. For GEO, it increases AI citation volume by providing structured, unambiguous answers that models can trust.
What’s the difference between schema markup and metadata?
Metadata (like title tags and meta descriptions) describes a page to search engines but isn’t designed for complex, structured relationships. Schema markup explicitly defines entities, attributes, and relationships, giving search engines and AI much richer context.
Is schema markup a ranking factor?
Not directly. Schema itself won’t improve your rankings, but by enhancing SERP features and CTR, it can indirectly support better performance.
Which schema markup language does Google prefer?
Google recommends JSON-LD because it’s clean, separate from HTML, and easy to maintain, though Microdata and RDFa are also supported.