Does ChatGPT pose a real threat to Google?
ChatGPT has successfully disrupted many industries with its functionality, including Google. We dive into how the platforms differ and how Google has responded to OpenAI's chatbot encroaching on Search.
Updated March 14, 2025

AI Summary
ChatGPT introduced a completely new model that may have the potential to chew away at Google's search traffic. In fact, Microsoft’s CEO Satya Nadella says that each user migration from Google to ChatGPT increases Microsoft's margin. This dynamic raises key questions:
- Is ChatGPT a genuine threat?
- Will it persist as a long-term threat?
- How will it impact the market?
To answer these questions comprehensively, we must first understand how ChatGPT operates and compare it with Google.
Key takeaways
- ChatGPT introduced an innovative process for understanding and answering questions.
- Google has superior capabilities, with more than enough potential to catch up to ChatGPT.
- ChatGPT has forced Google to innovate, shaping a new era in Search.
- Google combining chat and Search is a strategic response to ChatGPT.
How ChatGPT operates
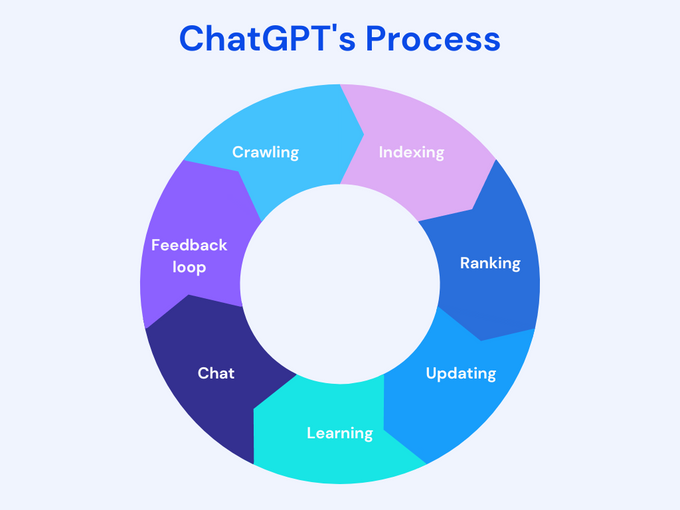
ChatGPT essentially digests the entire web, learning and storing the information it encounters to answer queries. Here's how it works:
1. Crawling
ChatGPT crawls as many websites as possible, scraping every bit of information. As of now, it has crawled information up to 2021.
2. Indexing
It then sorts this data into databases so that it can pull out the information it needs and use it to answer our questions. It's like a digital YellowPages, with everything neatly filed away for easy access.
3. Ranking
Next, ChatGPT takes all of this indexed information—some of which may be overlapping, duplicated, or low quality—and ranks it. It compares different sources and determines the accuracy and depth of each. This ranking helps the model discern which information is valuable for learning.
4. Updating
ChatGPT continually refreshes its databases to account for changes and updates.
5. Learning
With data indexed and ranked, the AI magic happens. The model can learn from it and draw conclusions.
6. Chat
We're all familiar with this part. You ask the AI chatbot questions, and it answers, not by pulling up links but by understanding the information and formulating responses. This approach is based on understanding and memory, which sets it apart from a traditional search engine.
7. Feedback loop
ChatGPT learns from every interaction. It continuously refines its responses by assessing where answers were sufficient or lacking. This feedback loop is vital to the process, ensuring continuous improvement and preventing the model from providing subpar answers.
Google beats ChatGPT across the board
Aside from learning and answering queries, ChatGPT's functions aren't that different from search engines like Google, a company with a 25-year monopoly dominating 82% of the market. So, how does Google stack up against ChatGPT?
» Find out if ChatGPT will affect Google's profits.
1. Crawling
Google excels here, crawling 1.12 billion websites and 50 billion web pages on the internet every day.
2. Indexing
Since Google crawls the entire internet regularly, it has unmatched indexing capabilities far superior to any other company, including OpenAI.
3. Ranking
Google's Search ranking algorithms are top-tier, with hundreds working in harmony. As evidenced by the quality of its search results, Google outperforms its competitors.
4. Updating
Google can almost instantly update news events and surface them in its search results, outperforming ChatGPT's more limited database.
5. Learning
Google has incorporated AI into Search for over a decade, according to the latest Google I/O. One of their goals is to implement AI in Search in as many places as possible. While OpenAI may have surprised them with a more advanced model, Google's capabilities shouldn't be underestimated.
6. Chat
Google embraced the changes other platforms had started implementing by creating its own new way to search with AI-powered chat. Search Generative Experience (SGE) is Google's response to how search is changing.
7. Feedback loop
Google recognized the value of the feedback loop long ago, which is why Google owns at least six products where they can track user behavior with over a billion active users monthly: Chrome, Search, YouTube, Android, Maps, and Google Play. Google invested in these products to be part of the daily routine of billions of people to track user behavior in as many places as possible.
While Google is far ahead in terms of development and investment, its competition with ChatGPT mainly lies in learning and responding to queries. If Google hasn't caught up yet, it won't be long.
» Explore how ChatGPT is rewriting the rules of content marketing.
Google’s new search experience
At the latest Google I/O, Google announced a revamped search experience that blends AI chat with Search, embedding results like products, videos, articles, and locations directly into the chat.
It will also integrate chat with image generation and export chat content into Gmail conversations, Google Docs, and Google Sheets.
While ChatGPT could potentially develop these features with Bing, Google's superior search capabilities and a wide array of integrable products give it a distinct edge.
» Compare Google Gemini vs. ChatGPT and find out which chatbot is better.
What’s next?
We believe Google will emerge as the leader in integrating chat with Search, a major shift largely influenced by ChatGPT. While we don't see ChatGPT as a direct threat to Google, it has undoubtedly prompted Google to innovate. This leads to an influx of new products, services, and features, bringing a new era of Search. However, this shift also introduces a few challenges, such as intellectual property rights and the need to maintain relationships with publishers and the web in general.
READ MORE: ChatGPT search vs. Google: What’s the difference?